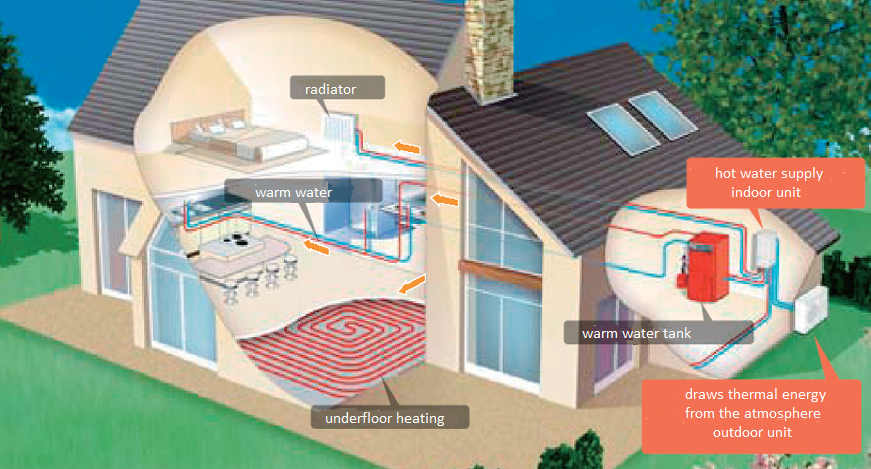
Basic principle of heat pump technology
Thermal energy as the basis of the hot water cycle
In the outdoor unit, the heat pump extracts the heat from the outdoor area and transfers it to the house as heating energy by means of a second circuit.
With the help of this heating energy, the hot water supply of the house is created via the indoor unit. The warm water now feeds the respective heating and supply circuits.
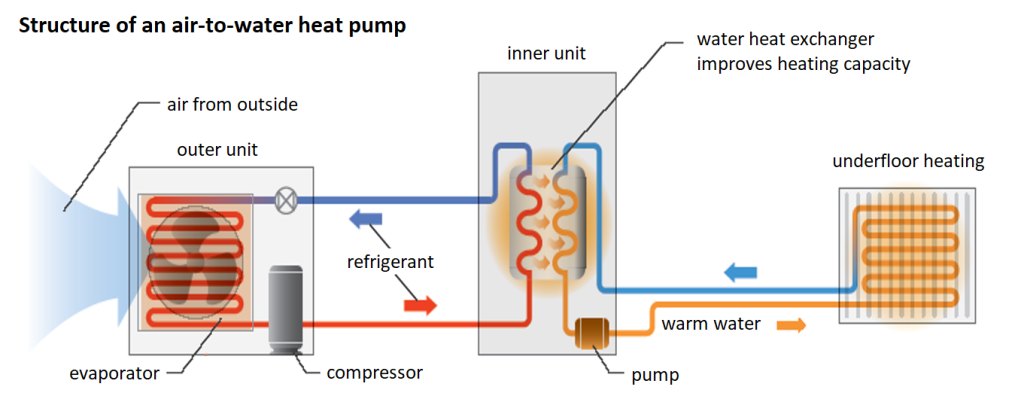
Overview function mode of a heat pump
Step 1: Environmental energy evaporates refrigerant
Step 2: Compressor compresses refrigerant vapor
Step 3: Heat pump heats the heating water
Step 4: Circuit of the air heat pump function

Indoor unit
Once the refrigerant steam has reached the required temperature, it flows through another heat exchanger. Here it feeds the transported thermal energy into the heating system, whereby the refrigerant itself cools down. At the same time, the pressure also drops and the medium gradually becomes liquid.
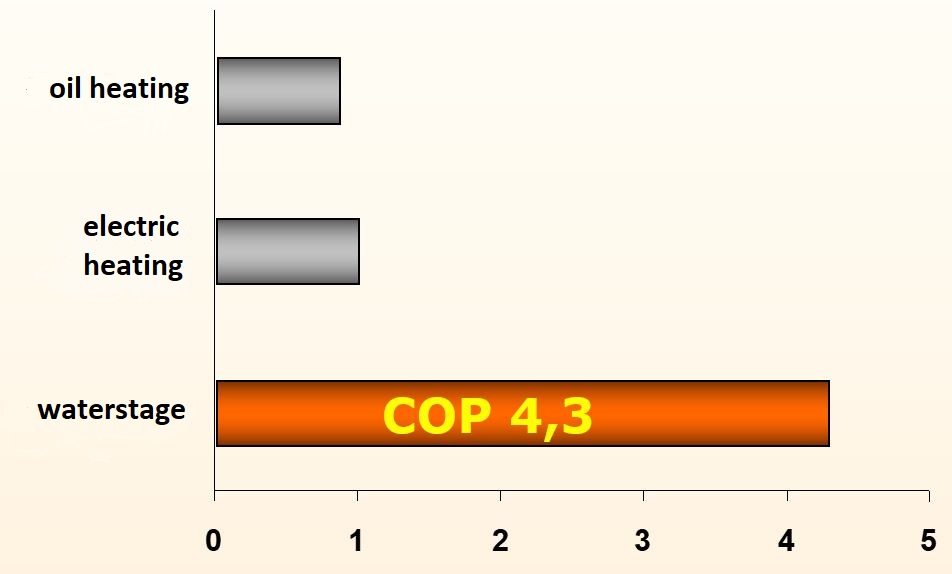
COP value
The COP value is the abbreviation for "Coefficient of Performance", which means efficiency of the heat pump. This key figure indicates the ratio between the heat output and the energy required to produce the heat output.

Monitoring and alarming
All parameters of this cycle like
- outdoor temperature
- individual flow temperatures within the circuit
- air humidity etc.
can be monitored. If a value exceeds or falls below the specified
range, an alarm is triggered immediately and appropriate
measures are initiated. In this way not only safety but also high
efficiency is guaranteed.